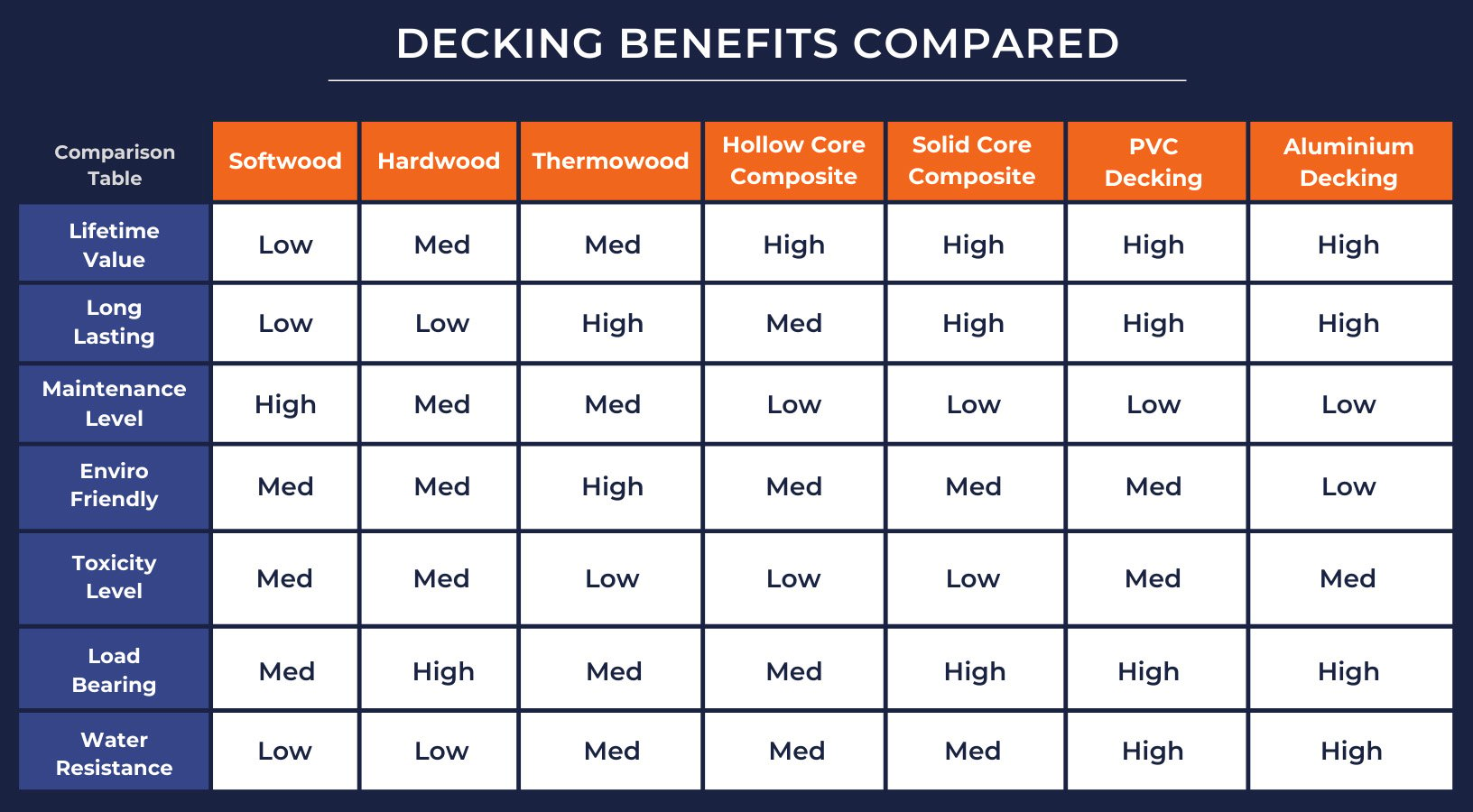
What is thermowood?
Thermowood is an engineered wood product that undergoes a specific treatment process to enhance its properties and durability. This innovative material is created by heating timber to high temperatures in a controlled environment, with exposure to steam. The result is wood that is more resistant to moisture, decay, and warping than traditional untreated timber. Its unique manufacturing process improves the wood’s physical characteristics while contributing to environmental sustainability, as it typically uses no chemicals in the treatment.
Unlike conventional lumber, thermowood is classified under durability standards, demonstrating superior performance in various climates. It is particularly beneficial for outdoor applications such as decking, siding, and furniture. The process minimizes the wood's equilibrium moisture content, reducing the likelihood of movement and damage from environmental factors. This background establishes a foundation for exploring why thermowood is an ideal choice for construction and design projects.
Why Choose Thermowood Boards
Thermowood offers numerous advantages, making it a compelling choice for consumers and builders alike. One of the primary benefits is its moisture resistance. Compared to untreated wood, thermowood has an equilibrium moisture content that is 40-50% lower. This results in significantly improved dimensional stability, reducing the wood's tendency to warp, swell, or shrink as moisture levels change—an important consideration in humid environments.
In terms of durability, thermowood is classified as durability class 2 under the EN 350-1 standard. This positions it as a viable alternative to pressure-treated wood products, allowing it to last up to 25 years or more, depending on application. Untreated wood, conversely, typically requires replacement every 5 to 10 years in challenging conditions. Additionally, thermowood possesses natural thermal insulation properties, offering energy efficiency benefits in both warm and cold climates. This combination of durability and energy efficiency, along with low maintenance requirements, makes thermowood an attractive option for various building projects.
This chart illustrates the longevity and maintenance needs of thermowood versus traditional wood (Source: Cladco Decking).
Thermowood versus Ordinary Wood
When comparing thermowood to untreated wood, thermowood shows notable advantages in performance and longevity. In various climatic conditions, thermowood retains its structural integrity better than untreated wood. For instance, it withstands freeze-thaw cycles in cold climates without damage, and in humid areas, it is less susceptible to rot and fungal growth. This significantly extends its lifespan compared to ordinary wood.
Moreover, while untreated wood demands frequent replacement due to damage and decay, thermowood can endure adverse conditions for over 25 years. Its maintenance requirements are also reduced, as it does not necessitate frequent resealing or treatment. This resilience in diverse climates makes thermowood a preferred choice for sustainable construction, enhancing its appeal over conventional untreated wood.
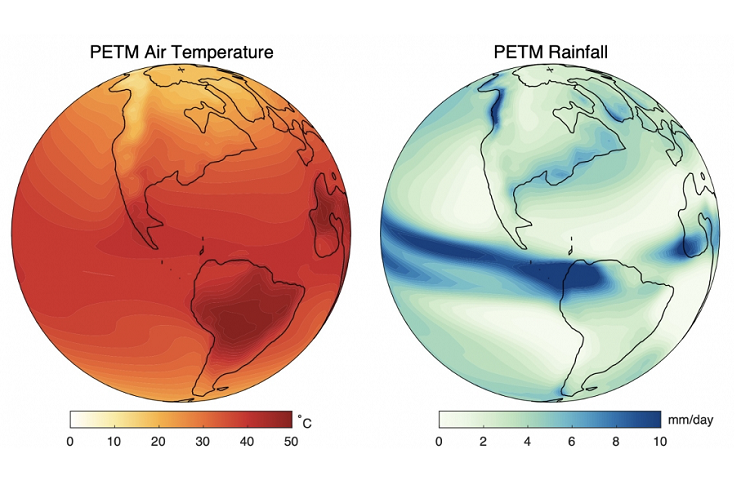
This climate map shows how thermowood performs best in different climates (Source: St Andrews University).
The Environmental Edge of Thermowood
Thermowood provides significant ecological benefits, particularly through its reduced carbon footprint. Its production process relies solely on heat and steam, resulting in a cradle-to-gate greenhouse gas emission of -653 kg CO2 per cubic meter. This negative value indicates that thermowood actively contributes to carbon sequestration, functioning as a carbon sink, unlike traditional materials, which have higher emissions.
Additionally, thermowood is fully recyclable, and its production process generates minimal waste. By using sustainably sourced timber, thermowood helps preserve forests and mitigate the environmental impact associated with deforestation. This combination of sustainability, reduced energy consumption, and lower emissions makes thermowood a leading choice among eco-friendly building materials.

This life cycle assessment scenario showcases the ecological impacts of heat-treated wood products compared to traditional materials (Source: Elsevier).
Innovative Techniques Elevating Thermowood Production
The production of thermowood incorporates advanced techniques that enhance both sustainability and performance. One of the most notable methods is the Westwood Process, which optimizes thermal modification to achieve specific results across various wood types. This automated system ensures consistent quality, making thermowood suitable for a wide range of applications.
In addition to advanced thermal modification, manufacturers are integrating green energy solutions to power their production processes, further reducing their ecological footprint. These innovations not only improve the quality of thermowood products but also support the industry's focus on sustainability. Manufacturers develop custom treatment protocols based on wood species and intended uses to enhance performance further.

This image captures a modern Thermowood production facility showcasing advanced kilns and machinery used for thermal modification (Source: Elsevier).
Real-World Applications: Success Stories of Thermowood in Architecture
Thermowood has been successfully utilized in various architectural projects, demonstrating its versatility and aesthetic appeal. One prominent example is the Thermowood House in Portugal, which blends seamlessly with its forested surroundings. This structure showcases the durability and beauty of thermowood while employing eco-friendly practices, as it is clad entirely in dark thermowood without chemical treatments.
Another notable application is the Powerhouse Telemark in Norway. This building features thermowood cladding that reflects sustainable design principles. In this case, the construction generates more power than it consumes, illustrating the material's functionality and positive environmental impact. Such projects exemplify how thermowood can enhance building quality while contributing to sustainable development.

This image illustrates a thermowood facade showcasing both beauty and durability in architectural design (Source: Lunawood).
Why Thermowood is the Smart Choice for Your Next Project
In conclusion, thermowood presents significant advantages over traditional untreated wood and modified wood products. With its exceptional moisture resistance, durability, thermal insulation properties, and low maintenance needs, thermowood is increasingly being adopted in various construction projects. Furthermore, the environmental benefits, including a negative carbon footprint and recyclability, support the growing market for sustainable building materials.
For architects, builders, and consumers, considering thermowood in design and construction can lead to more durable and environmentally friendly projects. Its complexity and innovation in production techniques, along with successful real-world applications, reinforce its status as a prime choice in modern architecture. As awareness and availability of thermowood grow, it remains a resourceful option for a wide range of design needs.

This image invites readers to explore Thermowood for their projects, reflecting its appeal and quality (Source: SpecifiedBy).
